Mach-O里与方法有关的Load Command有两种类型,LC_MAIN 和 LC_FUNCTION_STARTS。 ####LC_MAIN LC_MAIN是描述可执行文件的入口函数int main(int argc, char * argv[])的,它的定义如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
struct entry_point_command {
uint32_t cmd; /* LC_MAIN only used in MH_EXECUTE filetypes */
uint32_t cmdsize; /* 24 */
uint64_t entryoff; /* file (__TEXT) offset of main() */
uint64_t stacksize;/* if not zero, initial stack size */
};
从定义上可以看到入口函数的地址计算公式,也即是
1
Entry Point = vm_addr(__TEXT) + entryOff + Slide
从dyld的源码里能看到对Entry Point的获取和调用
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
namespace dyldbootstrap {
uintptr_t start(const dyld3::MachOLoaded* appsMachHeader, int argc, const char* argv[],
const dyld3::MachOLoaded* dyldsMachHeader, uintptr_t* startGlue) {
//
// Entry point for dyld. The kernel loads dyld and jumps to __dyld_start which
// sets up some registers and call this function.
//
// Returns address of main() in target program which __dyld_start jumps to
//
uintptr_t
_main(const macho_header* mainExecutableMH, uintptr_t mainExecutableSlide,
int argc, const char* argv[], const char* envp[], const char* apple[],
uintptr_t* startGlue) {
// find entry point for main executable
result = (uintptr_t)sMainExecutable->getEntryFromLC_MAIN();
return result;
}
}
}
Entry Point的调用在dyldStartup.s里,有兴趣的可以深入看下。 ####LC_FUNCTION_STARTS 它的数据结构如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
#define LC_FUNCTION_STARTS 0x26 /* compressed table of function start addresses */
struct linkedit_data_command {
uint32_t cmd; /*LC_FUNCTION_STARTS, etc*/
uint32_t cmdsize; /* sizeof(struct linkedit_data_command) */
uint32_t dataoff; /* file offset of data in __LINKEDIT segment */
uint32_t datasize; /* file size of data in __LINKEDIT segment */
};
从注释上看到Load Command里的数据是函数地址列表。
使用MachOView查看 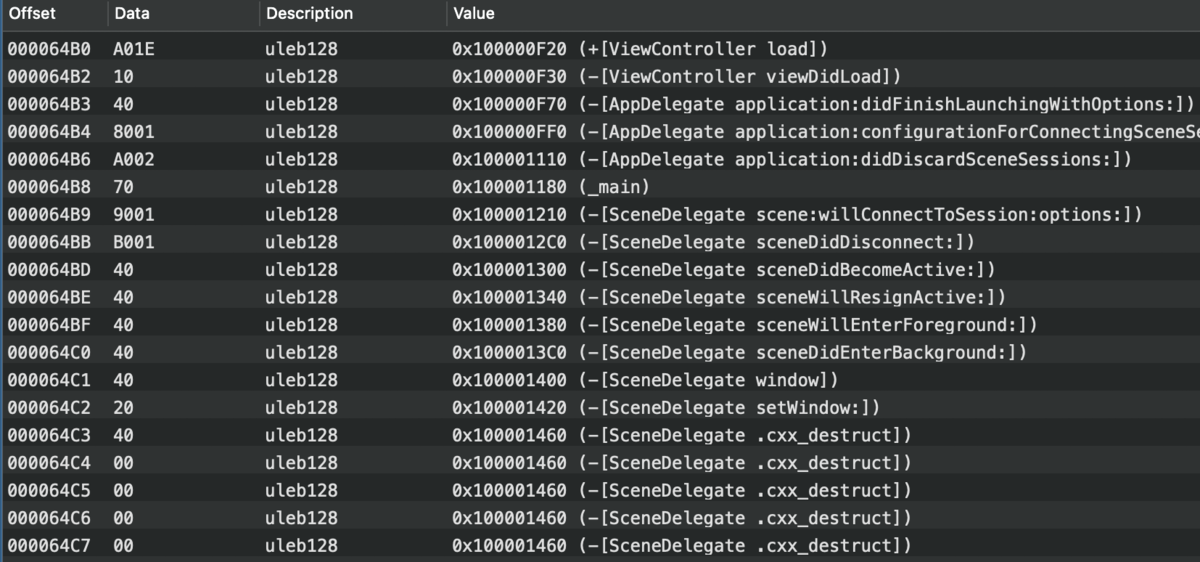 函数地址的计算公式是
函数地址的计算公式是function_addr = base_vm_addr + offset(累计)。 offset使用uleb128编码。uleb128是一种用变长字节(1-5)表示int类型的编码方式。详细介绍参考uleb128、sleb128和uleb128p1编码格式介绍、LEB128。 直接看dyld里的代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
template <typename A>
void DyldInfoPrinter<A>::printFunctionStartsInfo()
{
if ( (fFunctionStartsInfo == NULL) || (fFunctionStartsInfo->datasize() == 0) ) {
printf("no function starts info\n");
}
else {
const uint8_t* infoStart = (uint8_t*)fHeader + fFunctionStartsInfo->dataoff();
const uint8_t* infoEnd = &infoStart[fFunctionStartsInfo->datasize()];
uint64_t address = fBaseAddress;
for(const uint8_t* p = infoStart; (*p != 0) && (p < infoEnd); ) {
uint64_t delta = 0;
uint32_t shift = 0;
bool more = true;
do {
uint8_t byte = *p++;
delta |= ((byte & 0x7F) << shift);
shift += 7;
if ( byte < 0x80 ) {
address += delta;
printFunctionStartLine(address);
more = false;
}
} while (more);
}
}
}
方法的顺序在Linkmap里Symbols部分也能看到。 #####方法重排 链接器可以按照你指定的顺序排布方法,Xcode的设置如图: 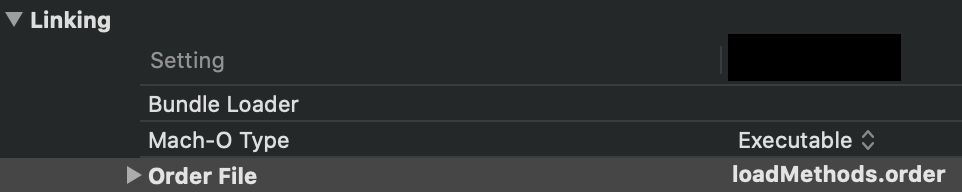 通过在Order File里指定方法的顺序,比如+load方法,或者是app启动时会调用的方法,可以达到加快启动速度的效果。详细内容参见AppOrderFiles和Improving App Performance with Order Files。
通过在Order File里指定方法的顺序,比如+load方法,或者是app启动时会调用的方法,可以达到加快启动速度的效果。详细内容参见AppOrderFiles和Improving App Performance with Order Files。